Introduction to Supply chain management:
Supply chain management (SCM) is the process of managing the flow of goods and services from the supplier to the end consumer. It involves coordinating and integrating various activities such as procurement, logistics, and inventory management to ensure that products are delivered to customers in a timely and cost-effective manner. Effective supply chain management can help organizations reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction. In this blog, we will discuss the key components of supply chain management and some best practices to optimize the supply chain.
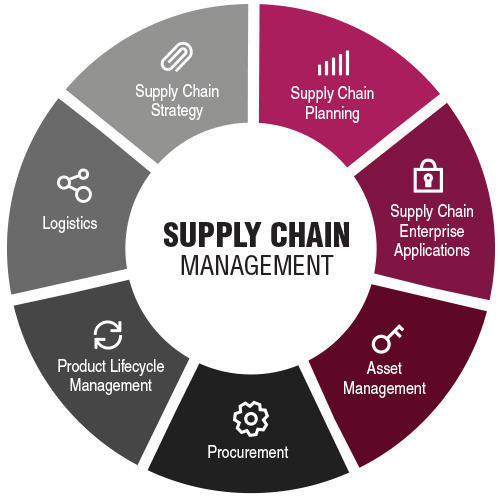
Key Components of Supply Chain Management:
Procurement (Supply chain management):
Procurement is the process of acquiring goods and services from suppliers. It includes activities such as sourcing, negotiating contracts, and managing relationships with suppliers. The procurement function is critical to ensuring that products are available when they are needed, and at the right price. The procurement function involves the following activities:
Sourcing: This involves identifying potential suppliers that can meet the organization’s needs.
Negotiating contracts: This involves negotiating contracts with suppliers to ensure that the organization gets the best price and terms.
Managing relationships with suppliers: This involves building and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers to ensure that products are delivered on time and at the right quality.
Logistics:
Logistics involves the transportation, warehousing, and distribution of goods. Logistics involves managing the physical movement of products from the supplier to the end consumer. It is important to ensure that the right products are delivered to the right location at the right time. The logistics function involves the following activities:
Transportation: This involves moving products from the supplier to the organization’s warehouses or distribution centers.
Warehousing: This involves storing products in warehouses or distribution centers before they are distributed to customers.
Distribution: This involves delivering products to customers.
Inventory Management:
Inventory management involves managing the level of inventory in the supply chain. Organizations need to balance the costs of holding inventory with the risks of stockouts. Effective inventory management can help organizations reduce costs and improve customer satisfaction. The inventory management function involves the following activities:
Forecasting demand: This involves forecasting customer demand for products to ensure that the right level of inventory is available to meet customer demand.
Order management: This involves managing orders to ensure that products are available when they are needed.
Inventory optimization: This involves optimizing inventory levels to reduce costs while ensuring that products are available when they are needed.
Demand Planning:
Demand planning involves forecasting customer demand for products. Demand planning is critical to ensuring that the right level of inventory is available to meet customer demand. It is important to have accurate demand forecasts to ensure that inventory levels are optimized. The demand planning function involves the following activities:
Forecasting demand: This involves forecasting customer demand for products to ensure that the right level of inventory is available to meet customer demand.
Collaborating with other functions: This involves working with other functions such as marketing and sales to ensure that demand forecasts are accurate.
Supplier Relationship Management:
Supplier relationship management involves managing relationships with suppliers. Organizations need to develop strong relationships with suppliers to ensure that products are delivered on time and at the right price. Effective supplier relationship management can help organizations reduce costs and improve the quality of products. The supplier relationship management function involves the following activities:
Supplier selection: This involves selecting suppliers that can meet the organization’s needs.
Supplier performance management: This involves monitoring supplier performance to ensure that products are delivered on time and at the right quality.
Supplier development: This involves working with suppliers to improve their performance and quality.
Have you heard about SAP & Oracle Consulting ? to know more click here...
Best Practices for Supply Chain Management:
Use Technology: Technology can help organizations improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain. The use of technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) can help organizations improve the visibility and transparency of the supply chain.
Develop Strong Relationships with Suppliers: Strong relationships with suppliers are critical to the success of the supply chain. Organizations need to develop relationships based on trust and transparency. This can help organizations reduce costs and improve the quality of products.
Focus on Continuous Improvement: The supply chain is constantly evolving, and organizations need to focus on continuous improvement. This involves regularly reviewing and optimizing the supply chain to ensure that it is meeting the needs of the organization.
Improve Collaboration: Effective collaboration between different functions in the organization is critical to the success of the supply chain. Organizations need to ensure that different functions such as procurement, logistics, and inventory management are working together effectively.
Monitor Key Performance Indicators: Organizations need to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure that the supply chain is operating effectively. KPIs such as on-time delivery, inventory turnover, and order accuracy can help organizations identify areas for improvement.
What are the 7 C’s of supply chain management?
The 7 C’s of Supply Chain Management are a framework that highlights key components and considerations for effective supply chain management. These components collectively contribute to the overall success and efficiency of the supply chain. The 7 C’s are as follows:
- Connectivity: Connectivity refers to the integration and collaboration between various entities within the supply chain, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. Effective connectivity ensures seamless flow of information, materials, and processes across the supply chain network.
- Collaboration: Collaboration emphasizes the importance of cooperation and coordination among supply chain partners. Collaborative relationships foster trust, shared goals, and mutual benefits. By working together, organizations can optimize processes, reduce costs, and enhance overall supply chain performance.
- Coordination: Coordination involves synchronizing activities and resources across the supply chain to achieve a seamless flow of goods and services. It entails aligning production schedules, inventory levels, transportation logistics, and other operational aspects to minimize delays, bottlenecks, and disruptions.
- Control: Control refers to having visibility and monitoring mechanisms in place to track and manage supply chain activities effectively. It involves implementing robust systems for monitoring inventory levels, demand forecasting, order processing, quality control, and performance metrics. With proper control mechanisms, organizations can identify issues and take corrective actions promptly.
- Customer Focus: Customer focus emphasizes understanding and meeting the needs and expectations of end customers. By aligning supply chain processes with customer demands, organizations can deliver products and services in a timely, efficient, and personalized manner. Customer focus includes aspects like demand forecasting, order fulfillment, delivery speed, and customer service.
- Cash Flow Management: Cash flow management involves optimizing the flow of financial resources within the supply chain. Efficient management of cash flow ensures that funds are available when needed, minimizing working capital requirements and improving overall financial performance. It includes aspects like payment terms, credit management, and financial risk mitigation.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuous improvement is the commitment to ongoing evaluation, refinement, and optimization of supply chain processes. It involves identifying areas for improvement, implementing best practices, embracing innovation and technology advancements, and fostering a culture of learning and adaptation.
By focusing on these 7 C’s, organizations can develop and maintain resilient, efficient, and customer-centric supply chains that drive business success and competitive advantage.
Conclusion:
Supply chain management is a critical function for organizations. Effective supply chain management can help organizations reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction. Key components of supply chain management include procurement, logistics, inventory management, demand planning, and supplier relationship management. Best practices for supply chain management include the use of technology, strong relationships with suppliers, focus on continuous improvement, improved collaboration, and monitoring key performance indicators. Organizations that focus on optimizing the supply chain can gain a competitive advantage in the market.